Accutane (Isotretinoin): Dosage Form, Mechanism of Action, Contraindications and Side effects, Food And Drug Interactions, Accutane in Pediatrics, Accutane and Pregnancy, Warnings and Precautions
CONTENT

- Spotlight on Accutane
- Dosage form
- Mechanism of action
- Accutane uses
- Administration and dosage
- Side Effects
- Accutane contraindications
- Accutane in pediatrics
- Accutane and pregnancy
- Accutane and breastfeeding
- Accutane interactions
- Warnings and precautions
- Overdose
- Accutane and weight changes
Spotlight on Accutane
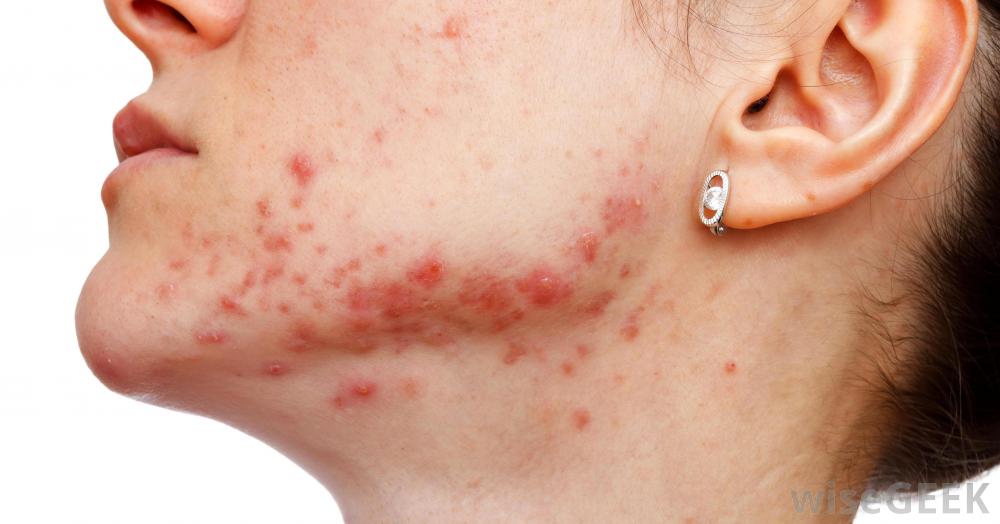
One of the most popular dermatologic medications, Accutane is the second-line treatment for seborrheic dermatitis, common acne, severe acne, rosacea, perioral dermatitis, and skin cancer. The vitamin A derivative (also referred as a retinoid), Accutane has an anti-inflammatory, anti-seborrheic, anti-microbial, and anti-comedogenic effect. From the chemical point of view, Accutane is 13-cis-retinoid acid.
Accutane dosage form
Accutane is a drug for the oral administration and is available in forms of 40 mg 20 mg, and 10 mg tablets. Generic Isotretinoin is also available in a form of 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 and 20 mg gelatin capsules or as a skin ointment.
Accutane mechanism of action
Also known as generic Isotretinoin, Accutane diminishes the production of sebum (skin oil) and simplifies its release. Put it medically, Accutane inhibits (blocks) the function of oil glands thus preventing hyperkeratinization. Molecules of Accutane cause apoptosis – the programmatic death of cells found in the sebaceous gland and boost the formation of NGAL – neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin – the protein that stops the generation of bacteria in the skin and on low levels of some inner organs.
Accutane uses
Accutane is indicated for the therapy of stubborn cystic acne and severe rosacea when the first-line medications prove to be ineffective against acne outbreaks. However, dermatologists often prescribe Accutane or its generics for mild and moderate comedones to help patients relieve keratosis and prevent skin scarring.
The off-label uses of Accutane include:
- hidradenitis suppurativa or acne inversa – clusters of swollen painful bumps under the skin;
- harlequin ichthyosis – a rare genetic disease characterized by the thickening of the keratin layer of the skin;
- lamellar exfoliation of the newborn – the dermatological disease causing skin drying and scaling in babies;
- xeroderma pigmentosum – an inherited condition under which skin is intolerant of ultraviolet light;
- Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva – a serious condition when connective tissue is replaced by bone tissue;
- Neuroblastoma – the nerve tissue cancer;
- Venereal warts – skin soft growths in the genital area;
- recalcitrant condylomata acuminata of the cervix – anogenital warts, the manifestations of human papillomavirus.
Accutane administration and dosage
 Owing to great lipophilicity (affinity for fats), Accutane is quickly absorbed especially when consumed with a high-fat food. If taken without a meal, the absorption of Accutane reduces twice compared to the co-administration with a meal.
Owing to great lipophilicity (affinity for fats), Accutane is quickly absorbed especially when consumed with a high-fat food. If taken without a meal, the absorption of Accutane reduces twice compared to the co-administration with a meal.
The Accutane dosage depends upon a patient’s weight and is calculated by the next formula: 0.5 mg (or 1 mg) of Accutane per 1 kg of weight a day. The ultimate total dose is recommended to be divided into two-three doses taken with a food. The course may last for 6 – 10 months depending on the treatment effectiveness.
In the pre-marketing trials, even the lowest dose of Accutane (0.1 mg) proved to relieve the development of the disease with an evident clearing of acne eruption. Dose adjustments may be required according to an individual response to Accutane or when some adverse events occur.
If acne outbreaks are severe or there is a risk of scarring, then the doctor may recommend increasing the dose up to 2 mg/kg provided a patient tolerates Isotretinoin well.
For the best therapeutic benefit, Accutane is advised to be used 2 – 3 times per day.
In pre-marketing research, Accutane was reported to reduce the total count of acne by 75 % in 15 – 20 weeks after the treatment onset. In this case, patients are recommended to discontinue taking Accutane. If persistent acne recurs in several months after the therapy, one more course of Accutane may be prescribed.
The long-term treatment or retreatment with Accutane or its generics is not recommended for those individuals who have not yet completed their skeletal growth as the drug is suspected of causing bones fragility.
Accutane side-effects
Accutane general adverse effects are similar to the overdose of Vitamin A and include skin dryness, allergic reactions, insignificant loss of weight, light sensitiveness, and easy fatigability. Adverse events are reversible once the treatment is discontinued.
Nervous system and sensory organs
Common: headache, undue fatigability, a rise of intracranial pressure (pseudotumour cerebri: migraine, nausea, vomiting, vision disturbance, optic disc edema), seizures, xerophthalmia, visual acuity failure, a dread of light, eye irritation, night vision impairment.
Rare: low spirits, depression, aggressive behavior, psychosis, suicidal ideation, emotional imbalance, colorblindness, lenticular cataract, corneitis, psorophthalmia, conjunctivitis, optic neuritis, hearing impairment.
Hematologic
Common: anemia, leukocytopenia, neutropenia, alterations (either an increase or a drop) in the number of platelets, acceleration of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), neutrocytopenia.
Rare: malignant granulocytopenia.
Musculoskeletal system
Common: muscle pain with or without elevation of serum CK level, painful joints, bony overgrowth, arthritis, calcification of tendons and ligaments, tenositis, brittleness of bone, chest pains.
Rare: rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown).
Respiratory
Rare: bronchial spasm (typically, in patients with a past history of asthma), voice alterations, respiratory tract infections.
Gastrointestinal
Common: dry mouth, gum inflammation and bleeding, nausea, diarrhea, inflammatory bowel diseases including colitis and ileitis, and pancreatitis.
Rare: incidents of pancreatitis with followed by death, transient and reversible increase of hepatic transaminases, isolated cases of hepatitis. Under these circumstances, it is advisable to reduce the dose or cancel the drug.
Skin integuments
Common: palms and soles exfoliation, skin rash and itching, face erythema/dermatitis, excessive sweetening, pyogenic granuloma, paronychia, dystrophic onychia, persistent thinning of hair, reversible hair loss, fulminant forms of acne, hirsuties, hyperpigmentation, photosensitivity, bruising. At the treatment beginning, there may be acne exacerbation, which may last for several days.
Rare: easy skin vulnerability, prolonged wound healing.
Other
Bloody urine, protienurea, allergic vasculitis, recurring hypersensitivity reactions, Bright disease, infections caused by gram-positive pathogens (Staphylococcus aureus), cholesteremia, hyperuricemia, a decrease of high-density lipoproteins, hyperglycaemia.
Accutane contraindications
A long-term treatment with Accutane is contraindicated for people suffering from:
- diabetes;
- depression and other psychiatric disorders;
- obesity;
- lipid storage disease;
- alcoholism;
- intracranial hypertension;
- osteoporosis and other bone metabolism diseases;
- liver conditions;
- individual intolerance of Accutane or its components.
Accutane in pediatrics
The therapy with Accutane for persistent cystic acne is not recommended for children under 17 as they have not yet completed their skeleton development because the medication is reported to cause a significant (up to 4 %) decrease in the bone density.
Accutane and pregnancy
 Accutane and its generics are contraindicated for pregnant women and for those who are planning for pregnancy. The lowest doses of Accutane are proved to cause severe birth defects in a fetus.
Accutane and its generics are contraindicated for pregnant women and for those who are planning for pregnancy. The lowest doses of Accutane are proved to cause severe birth defects in a fetus.
There is documentary evidence that Accutane induces the following congenital deformity in unborn children:
- physical defects of the eyes, face, skull;
- central nervous system impairments, cranial nerve deficit, and cerebral malformation;
- congenital pathology of a cardiovascular system;
- mental development disorder;
- ear deformation;
- cleft of the hard palate;
- hydrocephaly;
- microcephalism;
- malformation of throat sweetbread.
If a woman gets pregnant while being on Accutane, she must discontinue the medication immediately and seek for the consultation with a medical specialist experienced in reproductive toxicology.
During the Accutane oral treatment, it is highly recommended for females to use two effective forms of contraception, say condoms and birth control products.
Accutane and breastfeeding
There is no evidence if Accutane is excreted in the breast milk that is why nursing mothers are not recommended to use Accutane in order to eliminate the risk of adverse reactions in babies.
Accutane interactions
The concomitant use of Accutane with other retinoids (including acitretin, tretinoin, retinol, adapalene) increases the risk of vitamin A hypervitaminosis.
Severe drug interactions are possible when Accutane is simultaneously taken with tetracycline antibiotics as there is a risk of increased intracranial pressure, which can result in the development of pseudotumour cerebri.
Accutane can negatively influence the effectiveness of progesterone; therefore, during the therapy with Isotretinoin, the use of contraceptives containing small doses of progesterone should be avoided.
The simultaneous use of Accutane with sulfonamides, tetracyclines, thiazide diuretics increases the risk of sunburn.
Seizure medications and steroids must not be concomitantly used with Accutane as well as there is a hazard of major drug-to-drug interactions.
Accutane must not be used together with alcohol as there is the potential of moderate adverse reactions including irregular heartbeat, facial flushing, vomiting.
Patients are advised to stop taking any vitamins and herbal supplements while on Accutane therapy as there is a risk of hypervitaminosis.
Accutane warnings and precautions
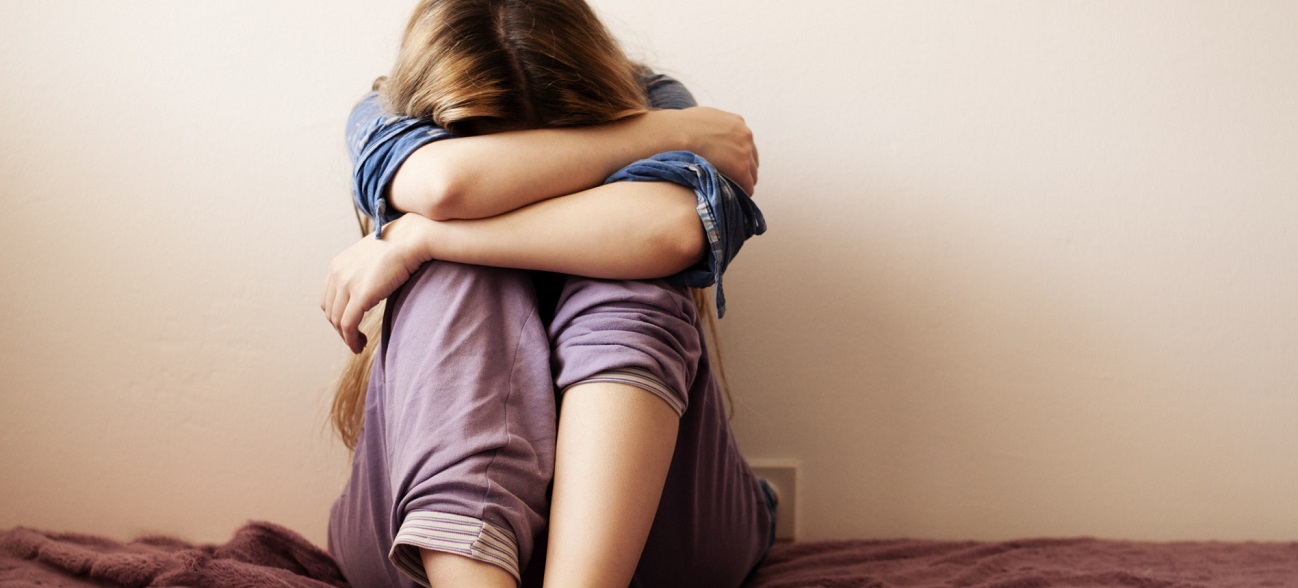

The systematic use of Accutane may initiate depressive syndrome, psychotic illness, suicidal thoughts and attempts, and violent behavior. Patients must make sure they do not suffer from any psychiatric disorder and do not have a recent history of mood disturbance.
An individual must discontinue taking Accutane immediately under the next symptoms:
- hopelessness;
- guilt feeling;
- loss if interest in life;
- easy tiredness;
- restlessness;
- touchiness;
- dangerous impulsivity;
- aggression;
- inability to concentrate.
Accutane is a prescription drug that can only be taken when first-line treatments for acne failed to help.
Dose adjustments of Accutane are required if a person:
- suffers or has a medical case of any mental illness;
- has any cardiovascular problems, diabetes or high cholesterol;
- has ever been diagnosed with bone disorders;
- has bowel, liver or respiratory conditions;
- experiences bleeding;
- complaints of eating disorder.
Patients must not donate blood while taking Accutane and for two months after the drug has been stopped.
Laser skin treatments and hair epilation procedures must be canceled during Accutane treatment as this is fraught with skin scarring.
Accutane makes skin very sensitive and easy vulnerable so that exposure to the direct sunlight and ultraviolet must be limited while on Isotretinoin for the avoidance of sunburn.
Accutane is associated with vision impairment so that a person must be very careful while driving a car or operating a dangerous machinery.
Males are required to use a condom or avoid reproductive sexual performance while taking Accutane because its active substance (Isotretinoin) is found in semen what may have a negative impact on the pregnancy onset.
Accutane overdose
If overdosed, Accutane may cause nausea and vomiting, face reddening, chilosis, dark and painful urination, stringent pain in the stomach area or in the whole body, headache, faintness, flu symptoms, skin blistering, and disturbance of muscular coordination.
Accutane and weight changes
There are no documented reports on the ability of Accutane to promote weight loss or gain. Though, the drug is known to influence mood and behavior what consequently may change a patient’s eating patterns. The only relationship between Accutane and weight alterations is that the drug dose is calculated based on a person’s weight.